By the way, what is indoor air pollution?
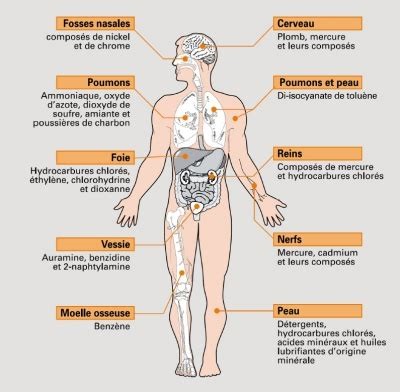
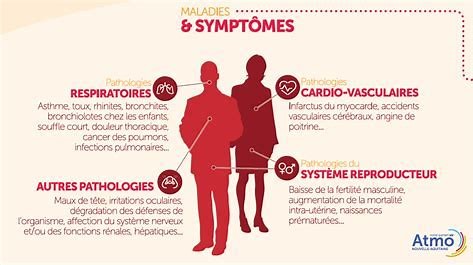
In 2014, the ANSES (National Agency for Food, Environmental and Occupational Health Safety) estimated the number of premature deaths caused by the best-known indoor air pollutants at around 20,000 per year. The air we breathe inside our homes can be of poorer quality than the air we breathe outside. This is due to some specific pollutants that emanate from the materials we use to build, decorate or furnish our homes. Also responsible for this indoor pollution are some of our activities: smoking, DIY, housework, etc.
Respiratory pollutants are of different types:
They are basically of three kinds:
- Chemical Pollutants
- Bio contaminants
- Physical Pollutants
Chemical Pollutants :
Our modern life contributes to the emergence of chemical pollutants.
The main outdoor chemical pollutants are :
- Ozone O3:
It is important to differentiate between upper-atmospheric ozone or stratospheric ozone, which is essential for life on earth, because it filters out a harmful part of the sun’s radiation, and ground-level ozone from the lower atmosphere, which is the pollution we breathe.
This form of pollution, known as secondary pollution, is subject to strong seasonal variations and exists especially in summer when the sun emits a lot of radiation. The sun’s ultraviolet rays transform certain primary air pollutants (hydrocarbons, nitrogen dioxide, etc.) into ozone.
- Nitrogen oxides NOx :
Nitrogen dioxide is the most abundant. It comes mainly from car traffic and, at present, especially from diesel vehicles, because unlike petrol vehicles, they are not equipped with catalytic exhaust systems that destroy this pollutant.
- Carbon monoxide CO :
It is the result of incomplete combustion (of cigarettes, petrol, coal, wood, etc.) in an insufficiently oxygenated environment: the carbon has only been able to fix a single oxygen atom (CO) whereas, in a sufficiently oxygenated environment, it combines with 2 oxygen atoms to form CO2.
- Sulfur dioxide SO2:
It is mainly produced during the combustion of fossil energy sources with a high sulphur content (coal, oil).
- Ammonia NH4 :
In air and in its gaseous state, ammonia helps neutralize other acid gases (such as SO2). In the soil, due to chemical reactions, it strongly modifies the soil.
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) :
Benzene C6H6 is one of the most dangerous VOCs for health, it is classified as a definite carcinogen. It is produced by fuel evaporation and road traffic.
Natural outdoor pollutants :
Pollution is not only a phenomenon attributable to human activities. Nature also produces its own pollutants that affect air quality in different ways.
Natural pollutants can be :
- mineral particles (sea spray, rock corrosion, soil erosion, volcanic ash, etc.).
- living particles (bacteria, viruses, microscopic fungi), plant particles such as pollens.
- Natural outdoor pollution has many origins
(Basement radon, volcanoes, sandstorms, fires, plants…).
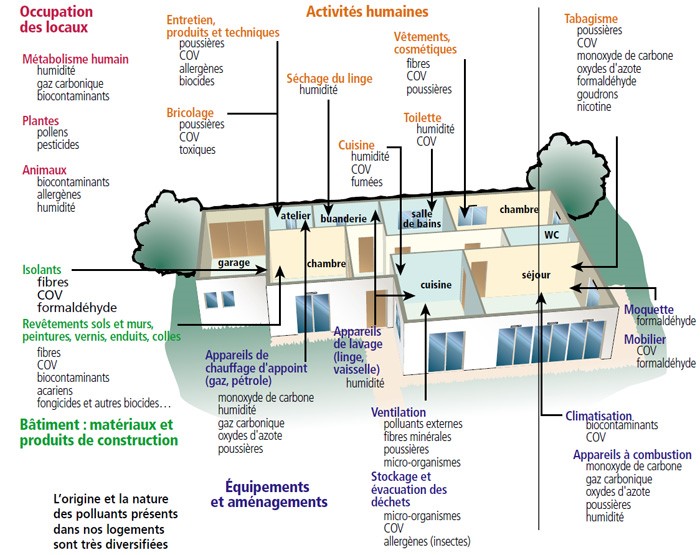
Indoor pollutants:
Indoor pollution is, in most cases, much higher than outdoor air pollution, but its composition is generally different due to the presence of specific pollutants.
Indoor pollutants come from a variety of sources:
- the penetration of outside air: motorized circulation, domestic heating, industrial companies.
- the air conditioning system which can, depending on its type and the regularity of its maintenance, improve or alter the quality of the air (mould, bacteria, dust)
- housing equipment (building materials, chipboard, insulation, varnishes and paints, household cleaning products or wood treatment products, etc.)
- human activity (physical activity, cooking, tobacco smoke…)
- bio contaminants (animals, plants…)
- various pollutants depending on the premises (asbestos, dust…)



0 Comments